
Dental Hygiene
When it comes to dental care and dental hygiene, the gums are often overlooked. After all, no one is taught from a young age to “brush and floss their gums.” Nonetheless, the gums are just as important, and susceptible to disease and decay if neglected, as a person’s teeth.
Diseased gums are often the underlying cause of bad teeth and not the other way around. Three out of four people or 75 percent of Americans suffer from some form of gum disease ranging in severity from mild gingivitis to advanced periodontal disease.
“3 out of 4 people or 75 percent of Americans suffer from some form of gum disease ranging in severity from mild gingivitis to advanced periodontal disease.”
Extrapolating these types of eye-opening statistics make gum disease one of the world’s most widespread oral afflictions. Despite its ubiquity, gum disease is often misunderstood and, as a result, undertreated.
About 3 percent of the afflicted population seeks treatment for their gum disease. In many cases, treatment isn’t sought until well after gum disease has entered an advanced stage known as periodontal disease or periodontitis. Once gum disease has progressed to this point, tooth loss may be unavoidable.
Remember, your gums cover and protect a tooth’s sensitive roots. When the gums are damaged and diseased, or have recessed below the roots, your teeth will suffer as well. Think of them as the soil in which your teeth are planted.
Many if not most of us have heard and been warned at one point in our lives to watch out for gum disease and “gingivitis.” A less common term is periodontitis. Most people have very little knowledge, unfamiliarity, or understanding of these terms and the impact they have on a person’s oral health. I want to provide you with a “Cliff’s Notes” version of these terms and what they mean for you.
Let’s get started.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease simply refers to an inflammation of the gums. Generally, this is caused by a buildup of bacteria at the gumline as a result of neglecting oral hygiene. Gingivitis and periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, are considered different types or stages of gum disease. When a doctor or dentist brings up gum disease, it is these two conditions that he is most likely referring although other oral conditions could also result in inflammation of the gums.
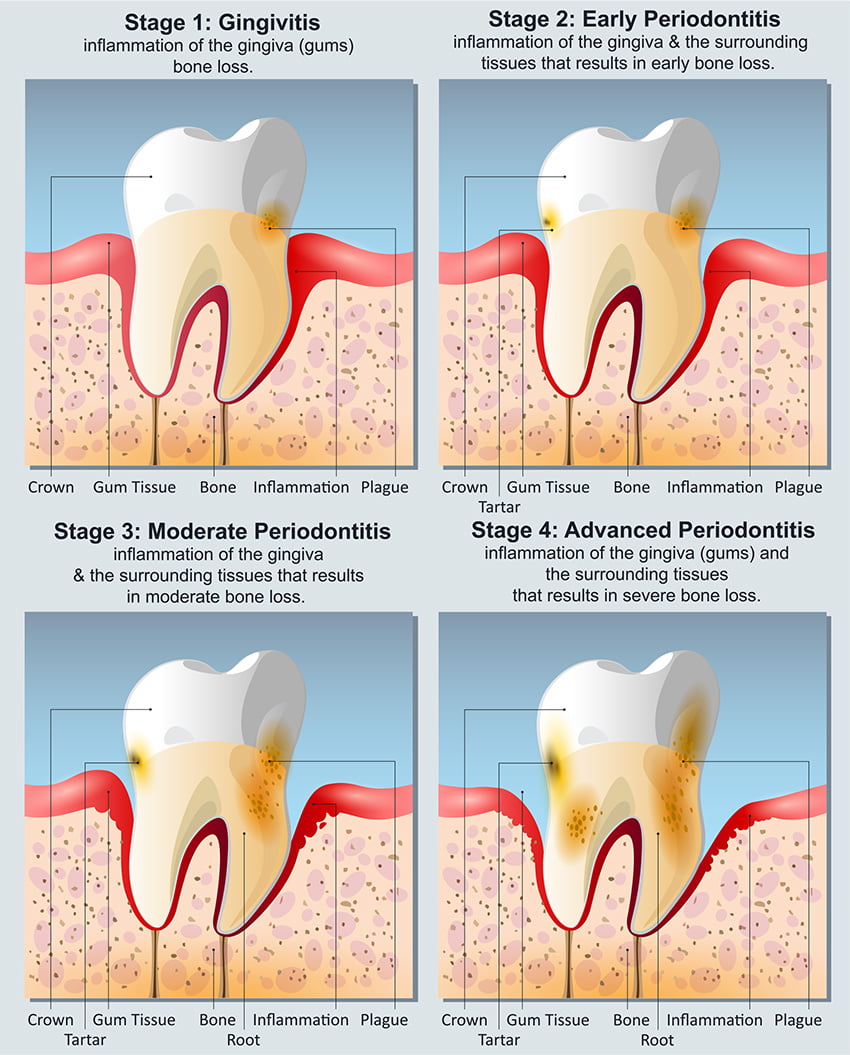
How are gingivitis and periodontal disease different?
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, while periodontal disease, or advanced periodontitis, may refer to gum disease in more advanced or later stages. As a result, untreated advanced periodontitis is considered much more severe than early-stage gingivitis.
But the differences don’t stop there.
Gingivitis
In the early stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, the gums become swollen and sensitive as a result of bacterial buildup. This can result in not only pain while flossing and brushing but bleeding as well.
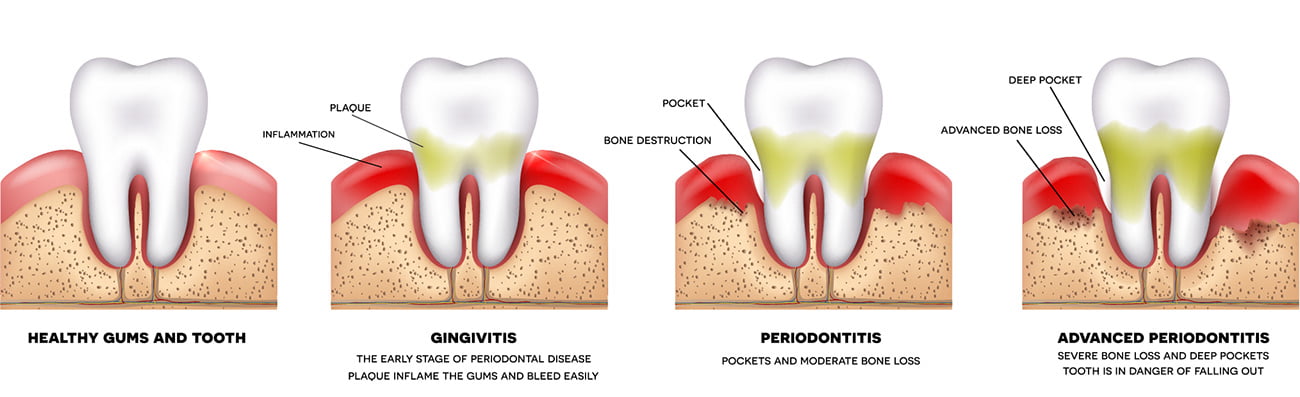
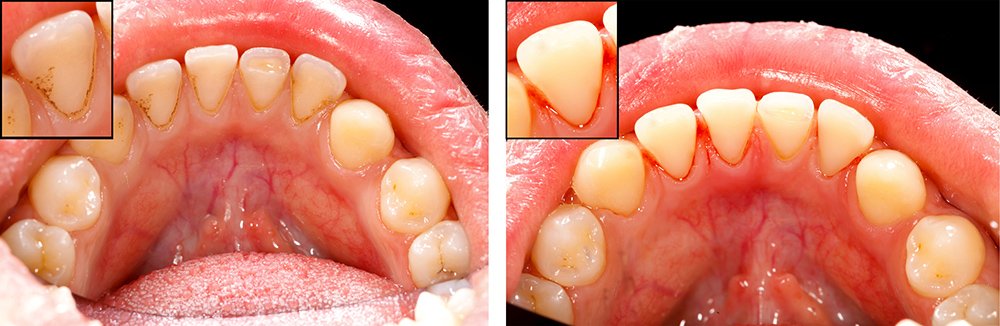
Bleeding gums despite proper brushing techniques is a sure sign of gingivitis. Fortunately, during this early stage of gum disease, the damage is reversible. With proper dental hygiene and regular visits to a dental clinic for professional dental exams and teeth cleanings (see teeth cleaning before and after photos below), gums can eventually heal and return to a healthy state.
Teeth Cleaning: Before and After Photos
Periodontal disease
Advanced gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is far different. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to full-blown periodontitis, which may cause irreversible damage.
Gums suffering from periodontitis are often characterized by areas of gum tissue that have separated from the underlying bone-forming pockets. These pockets trap debris and encourage additional bacterial growth leading to persistent infections.
Teeth Cleaning: Before and After Photos
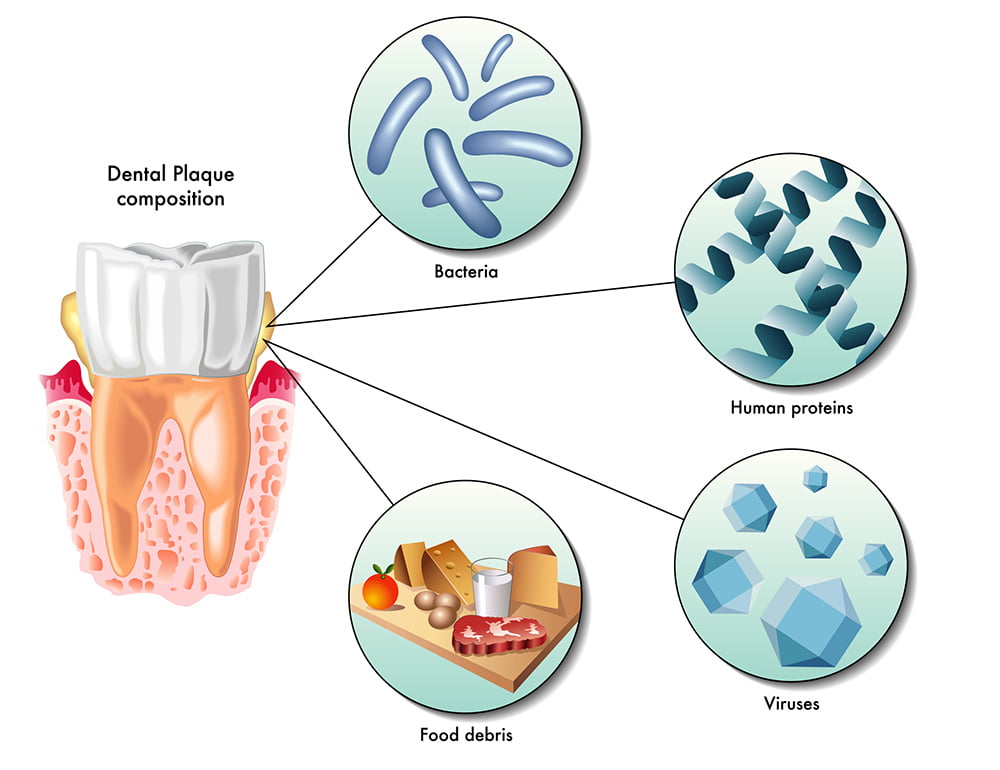
Periodontitis can be further categorized into three stages: early periodontitis, moderate periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Patients suffering from the former have experienced irreversible damage to the gum tissues and underlying bone. However, with improved dental hygiene and professional care, further damage can be limited, and infections contained.
With advanced periodontitis, the fibers and bones of the teeth themselves have been damaged or destroyed. This can result in teeth loosening and eventually falling out of their sockets.
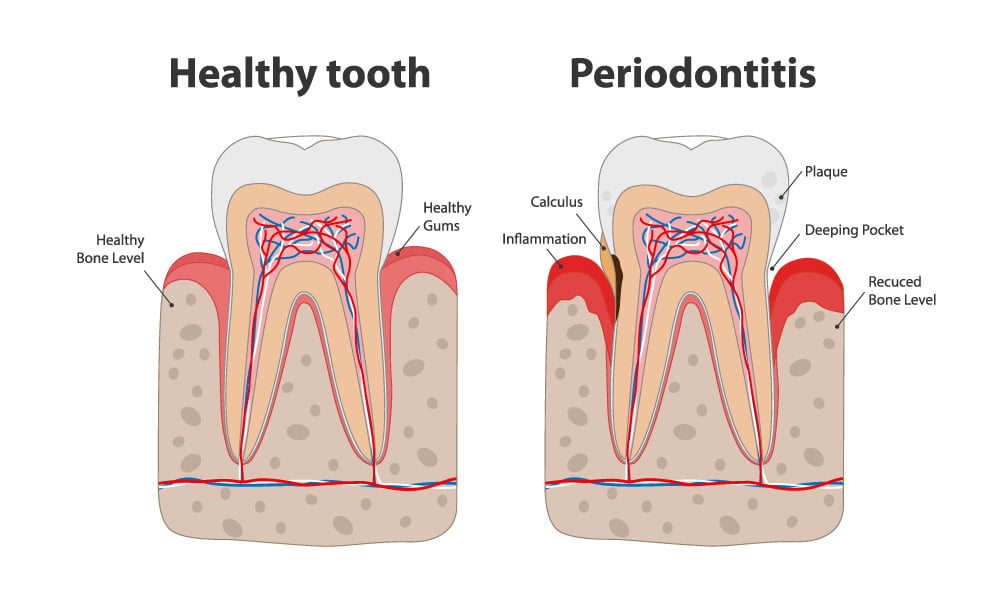
Remember, damage caused by gingivitis, including minor gum recession, can be reversed entirely with proper dental and oral hygiene.
Once gum disease has progressed from gingivitis to periodontal disease, the damage is permanent. That means that any gum recession, bone loss, and other dental damage caused by periodontitis cannot be reversed. That’s why timely and aggressive treatment and reversal of early-stage gum disease, or gingivitis, is so necessary.
Gum disease doesn’t just affect the gums and teeth. Like most systems in the human body, the gums are intimately and inextricably connected through nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and other interconnected systems to the rest of the body.
The importance of treating gum disease
Like many human diseases, early treatment is critical. Not only will taking gingivitis and gum disease seriously save your teeth, but it could also save your life. It has been found that patients with periodontal disease also suffer higher rates of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, pregnancy complications, and dementia.
Scientists have discovered a direct link between gum disease and heart disease in the form of bacterial endocarditis. As it turns out, bacteria in gum tissues can actually enter the bloodstream and settle on the heart’s valves. It has also been theorized that bacteria by way of infected gums can also attach to fatty deposits in the bloodstream leading to the formation of blood clots that may directly result in heart attacks and aneurysms.
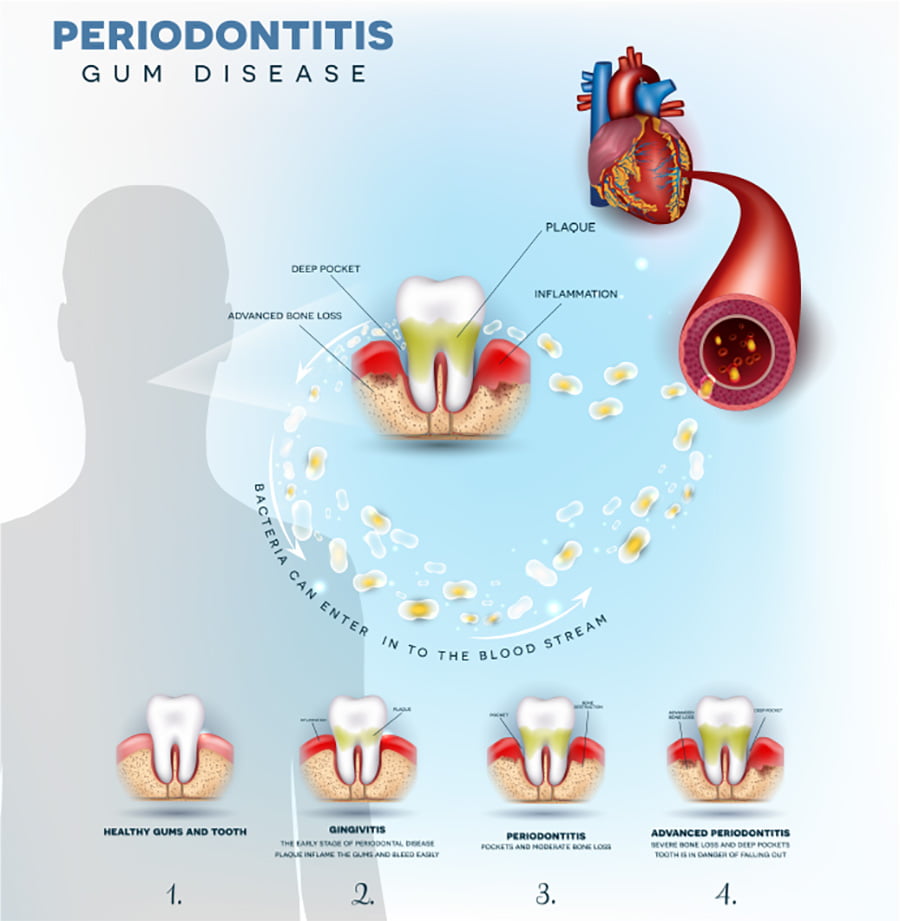
Taking good care of your gums is no more difficult than caring for your teeth. For healthy gums, brush and floss every day. Pay particular attention while brushing to bacterial buildup of plaque along the gumline which can irritate the gums over time or even spread beneath it.
When cleaning and examining your teeth and gums, be on the lookout for these signs of gingivitis and periodontitis, which I cover next.
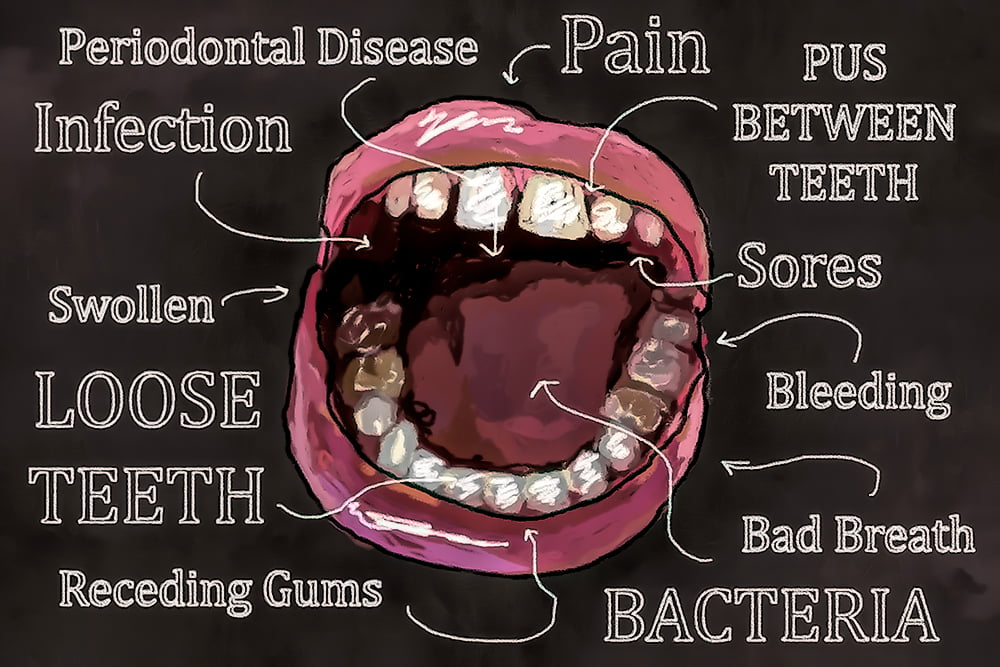
3 Signs of Gingivitis
Red, swollen gums

Sensitivity while brushing

Bleeding during flossing and brushing
Other signs of gingivitis include:
While these signs may be mild at first, gingivitis can worsen over time if left untreated. Monitoring for these symptoms is important to detect gingivitis early.
3 Signs of Periodontitis

Loose teeth

Viable gum recession

Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
Other signs of periodontitis include:
These advanced signs indicate destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth, including bone loss. Seeking treatment is important to try to halt the progression of damage.
 Written by Dr. Reza Khazaie
Written by Dr. Reza Khazaie